

Monitoring (signs, symptoms, progression/regression)Įvaluated (test results, response to treatment)Īssessment (condition of the patient, order test, referrals, review records)Īccurate coding is essential for characterizing the risk of the patient. One strategy that is commonly used by organizations to capture a diagnosis is the “ MEAT” method: The documentation in the patient’s medical record must support the condition as present and as being assessed and/or planned by an eligible provider qualified to manage the condition.
Examples of conditions that map to an HCC include: These providers must recapture ICD-10-CM codes for certain chronic conditions.
#Meat abbreviation in hcc coding code#
This encounter allows the appropriate ICD-10-CM code to be reported, and the HCC code to be captured, in the new base year. For example, a patient with CHF requires a face-to-face encounter each year, at which time the provider can discuss and document the CHF. Although chronic conditions are ongoing, providers must document a patient’s chronic condition and recapture the ICD-10-CM code annually to maintain the patient’s HCC risk score. Individual HCCs are valid for one year, regardless of the fundamental chronicity.
#Meat abbreviation in hcc coding download#
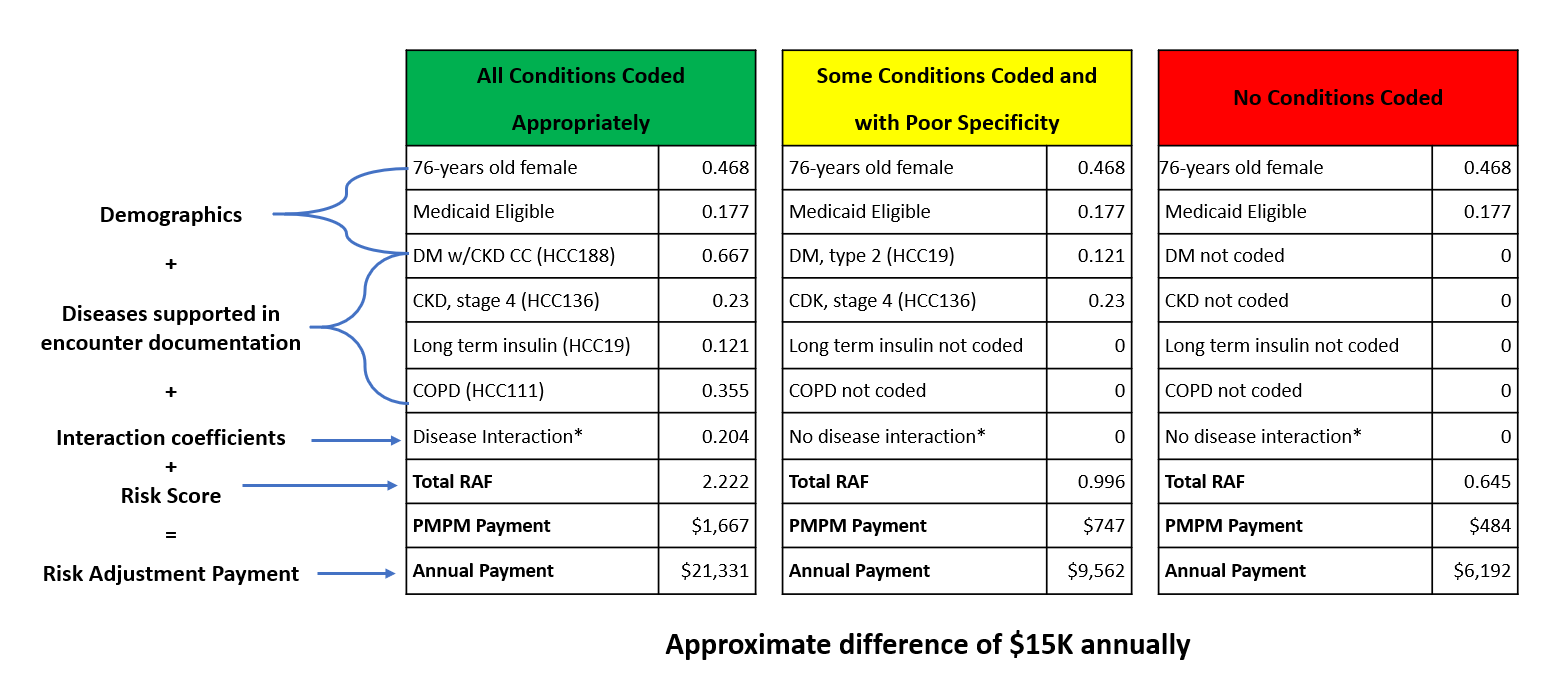
You can download the 2019 Mid-year Final ICD-10-CM mappings Excel file from the CMS website. Not all diagnoses are mapped to an HCC code, only the diagnoses that are costly to manage. Acute illnesses and injuries are not considered in this model because the data is not reliable when predicting healthcare costs. The CMS-HCC model focuses on chronic conditions, such as congestive heart failure (CHF) and diabetes, that impact future healthcare costs. The diagnostic groups are categorized into condition categories. HCC models organize the disease process and conditions into body systems and diagnostic groups. Healthcare facilities and plans use this model to understand the risk level of patients and predict patient cost. The CMS-HCC model relies on ICD-10-CM codes to map to HCC codes that risk adjust patients based on their state of health. Risk adjustment is a health plan process for compensation, based on the underlying health conditions of their enrollees. HCC is a risk adjustment model used by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) for Medicare Advantage (Part C) contract rates. Now is a perfect time to assess how your providers are documenting and reporting the health risks of their patients. The more accurate the risk scores, the more accurate the benchmark for expenditures, and the more accurate the physician’s reimbursement. In a value-based payment system, documentation - more specifically, coding extracted from that documentation - determines whether a physician is properly compensated for managing the chronically ill. Physician documentation is one of the most important keys when abstracting for hierarchical condition category (HCC) coding.

Documentation is key to correct ICD-10-CM coding, better patient care, and proper reimbursement.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
