

Chronic infection can be cured more than 95% of the time with antiviral medications such as sofosbuvir or simeprevir. Prevention includes harm reduction efforts among people who inject drugs, testing donated blood, and treatment of people with chronic infection. In the United States, screening for HCV infection is recommended in all adults age 18 to 79 years old. ĭiagnosis is by blood testing to look for either antibodies to the virus or viral RNA. It is one of five known hepatitis viruses: A, B, C, D, and E. It is not spread through breast milk, food, water or casual contact such as hugging, kissing and sharing food or drinks with an infected person. HCV may also be spread from an infected mother to her baby during birth. In regions where blood screening has been implemented, the risk of contracting HCV from a transfusion has dropped substantially to less than one per two million. HCV is spread primarily by blood-to-blood contact associated with injection drug use, poorly sterilized medical equipment, needlestick injuries in healthcare, and transfusions.
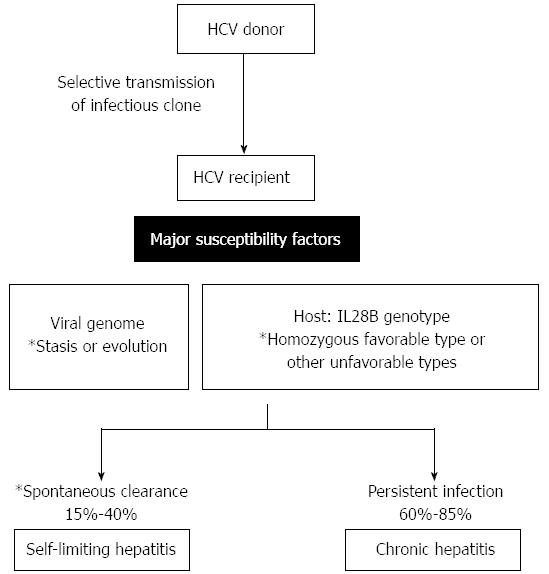
In some cases, those with cirrhosis will develop serious complications such as liver failure, liver cancer, or dilated blood vessels in the esophagus and stomach. Over many years however, it often leads to liver disease and occasionally cirrhosis. Early on, chronic infection typically has no symptoms. The virus persists in the liver, becoming chronic, in about 70% of those initially infected. Early symptoms can include fever, dark urine, abdominal pain, and yellow tinged skin. During the initial infection period, people often have mild or no symptoms. Hepatitis C is an infectious disease caused by the hepatitis C virus (HCV) that primarily affects the liver it is a type of viral hepatitis. Sterile needles, testing donated blood Īntivirals ( sofosbuvir, simeprevir, others) Hepatitis C virus usually spread by blood-to-blood contact īlood testing for antibodies or viral RNA Liver failure, liver cancer, esophageal and gastric varices Electron micrograph of hepatitis C virus from cell culture (scale = 50 nanometers)


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
